AWS WAF Challenge vs Cloudflare WAF: Key Differences
Compare AWS WAF's rule-and-token challenges with Cloudflare's risk-based Turnstile, plus differences in performance, integration, and pricing.

AWS WAF Challenge and Cloudflare WAF are two tools for protecting web applications from automated threats, but they work in different ways:
- AWS WAF Challenge: Uses rule-based systems and client-side computational tasks ("proof of work") to verify users. It issues a token to allow future access without repeated challenges.
- Cloudflare WAF: Relies on risk-based analysis and lightweight, privacy-friendly checks (like Turnstile) to identify bots without disrupting users.
Quick Comparison
| Feature | AWS WAF | Cloudflare WAF |
|---|---|---|
| Challenge Trigger | Rule-based, token validation | Risk analysis, client signals |
| Challenge Type | Silent tasks, occasional CAPTCHA | Invisible checks (Turnstile) |
| User Interaction | Minimal for silent tasks, required for CAPTCHA | Minimal, usually none |
| Bot Mitigation | Computational challenges | Adaptive traffic scoring |
| Pricing | Usage-based | Flat-rate plans |
| Integration | SDKs for apps | Browser-based |
Key takeaway: Choose AWS WAF for AWS-integrated environments and app-focused setups. Opt for Cloudflare WAF for simpler, flat-rate pricing and user-friendly operation.
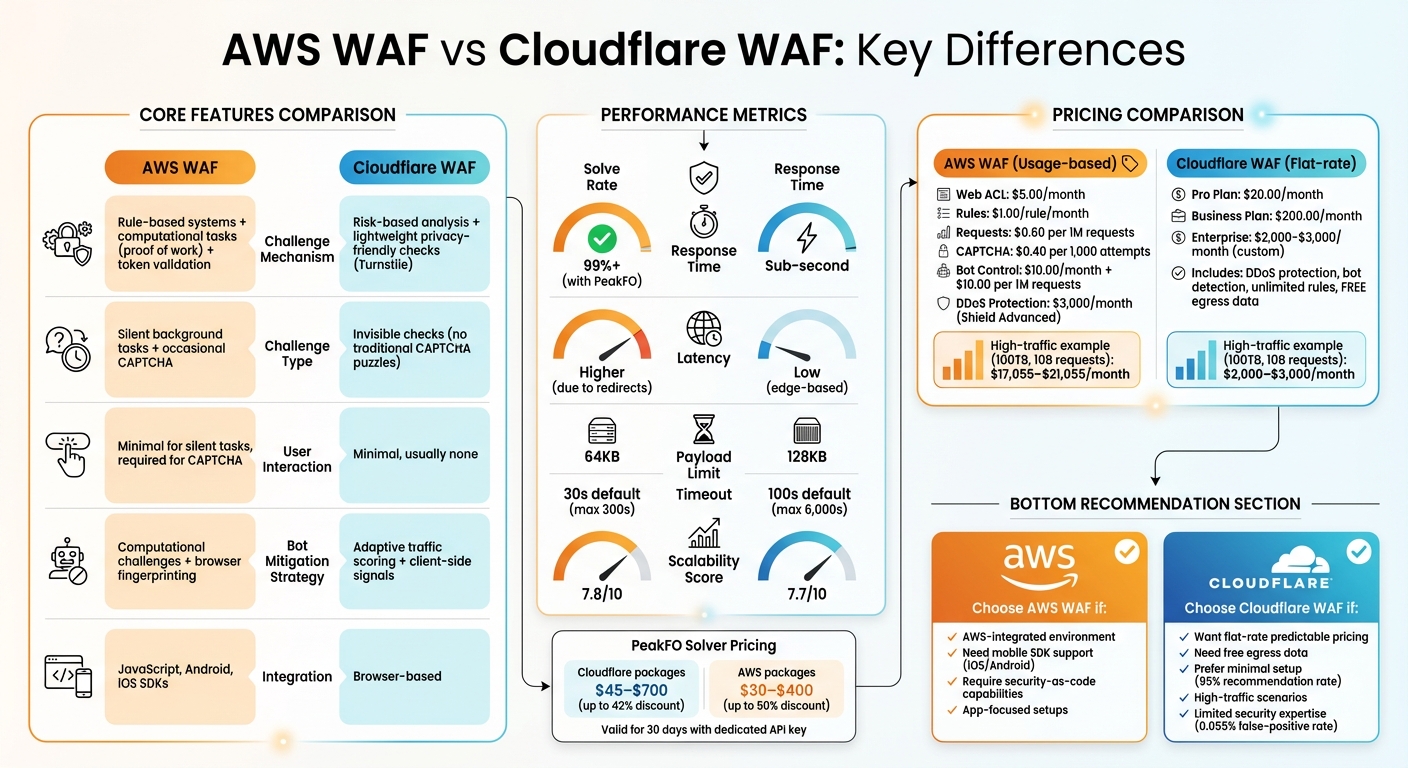
AWS WAF vs Cloudflare WAF: Complete Feature and Pricing Comparison
CAPTCHA Challenge Mechanisms Compared
Detection and Challenge Triggers
AWS WAF and Cloudflare WAF take different paths when deciding when to trigger a challenge. AWS WAF relies on specific rules and checks for a valid token. If a token is missing, invalid, or expired, the system evaluates the token's "immunity time" and executes a CAPTCHA or Challenge action if necessary. This approach is rule-driven and token-dependent.
Cloudflare, however, uses a dynamic, risk-based strategy. It evaluates client-side signals and browser environment details to assess whether a visitor is legitimate. This adaptive process adjusts to the perceived threat level of each user, offering a more flexible response compared to AWS's predefined rules.
AWS limits challenges to GET requests with text/html content, avoiding complications with POST requests and non-HTML data. It also recommends using CAPTCHA as a secondary measure for rate-based rules - setting a higher threshold for blocking and a lower one for CAPTCHA - to catch bots operating below the hard block limit.
Now, let's look at how each platform handles automated CAPTCHA-solving attempts.
Protection Against Automated Threats
AWS and Cloudflare take distinct approaches to thwart automated attempts to bypass CAPTCHA challenges. AWS WAF raises the bar for bots by incorporating a proof-of-work mechanism. It also uses browser fingerprinting - analyzing elements like browser plugins and JavaScript features - to detect signs of automation. To further secure endpoints, AWS offers JavaScript and mobile SDKs (for Android and iOS) to ensure tokens are correctly generated before requests reach the protected server, preventing bots from bypassing challenges through non-HTML traffic.
Cloudflare, on the other hand, avoids traditional CAPTCHA puzzles entirely. Instead, it employs Managed Challenges and its Turnstile system, which focus on lightweight, privacy-friendly verification methods. These systems ensure that most legitimate visitors pass without any manual interaction, reducing friction while still effectively blocking automated threats.
These differing strategies significantly impact how automation APIs interact with each platform's challenge mechanisms.
| Feature | AWS WAF | Cloudflare WAF |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Trigger | Rule-based inspection and token validation | Risk-based analysis of client-side signals |
| Challenge Types | Silent background or interactive CAPTCHA | Managed Challenges with Turnstile |
| User Interaction | Required for CAPTCHA; none for silent checks | Minimal; typically none unless flagged |
| Bot Mitigation Strategy | Increases computational effort for bots | Detects and mitigates automated traffic |
Cloudflare's focus on reducing user friction through silent verification and adaptive risk signals makes it harder for automated systems to predict when a challenge will occur. This approach contrasts with AWS's more structured, rule-based system, which emphasizes token validation and computational deterrents for bots.
Integration and Compatibility with Automated CAPTCHA Solving APIs
Integration Steps for AWS WAF and Cloudflare WAF
AWS WAF offers two main ways to integrate CAPTCHA challenges. The first, Interstitial Interaction, is straightforward and doesn’t require any code changes. AWS automatically serves a challenge page when necessary. The second option, Application Integration SDKs, provides more control for developers through JavaScript, Android, and iOS SDKs. This method is especially useful for Single Page Applications (SPAs), as it avoids unexpected fetch or XHR request errors caused by 202 or 405 HTTP responses.
Once a challenge is completed, AWS WAF generates an encrypted aws-waf-token cookie. Automated solving tools need to capture this token and include it in subsequent requests. Developers can either use AwsWafIntegration.getToken() to retrieve the token or rely on the AwsWafIntegration.fetch wrapper, which handles token inclusion automatically. For setups involving multiple subdomains - like www.example.com and api.example.com - configuring a shared token domain (e.g., .example.com) ensures the token works across all endpoints.
Cloudflare uses a different approach. Its Turnstile integration requires embedding a widget into the front-end and validating tokens on the server side. With Cloudflare's "Pre-Clearance" mode, the Turnstile widget can issue a clearance cookie before sensitive API calls, ensuring background fetch requests aren’t interrupted.
Both approaches are designed to work smoothly with automated API support, making the solving process efficient and reliable.
API Compatibility and Automation Support
PeakFO’s API is equipped to handle challenges from both AWS WAF and Cloudflare WAF. For AWS WAF, the service can solve JavaScript-based "proof of work" challenges or visual puzzles, returning the required session token. AWS WAF challenges are signaled by specific HTTP status codes: 202 Request Accepted for silent challenges and 405 Method Not Allowed for CAPTCHA puzzles. These responses also include the x-amzn-waf-action header.
However, there’s a key limitation to note: AWS WAF responses don’t include CORS headers. This prevents cross-domain JavaScript from accessing the headers needed to process challenges. Since standard browser fetch or XHR calls expect JSON or XML, they can’t natively handle the HTML required to render a CAPTCHA interstitial.
Understanding these technical nuances is crucial when configuring services and managing costs. PeakFO offers flexible pricing plans tailored for high-traffic scenarios. AWS WAF packages range from $30 to $400, with discounts of up to 50%. Cloudflare WAF packages range from $45 to $700, offering up to 42% in savings. Both include dedicated API keys and are valid for 30 days. Additionally, AWS WAF’s "immunity time" (default: 300 seconds) can be adjusted to balance security and solver API costs. Extending immunity time reduces the frequency of solver calls but increases the window for potential malicious activity.
"Solving a CAPTCHA can degrade your customer's website experience. So as part of best practices, we do recommend tuning your immunity time settings." – Connor Munros, Technical Account Manager, AWS
Performance and Effectiveness
Performance Metrics Comparison
When it comes to speed and reliability, both AWS WAF and Cloudflare WAF deliver sub-second response times and maintain over 99% success rates. However, the way they handle challenges and requests sets them apart.
AWS WAF relies on rule-based challenges that require redirects and additional evaluations. While effective, this approach introduces more latency. On the other hand, Cloudflare's Turnstile employs lightweight, privacy-focused challenges that operate at the edge. These often pass visitors automatically without requiring user interaction, making Cloudflare faster in scenarios where reducing friction is crucial.
Another key difference lies in how much data each can process. AWS WAF imposes a 64KB payload inspection limit and has a default response timeout of 30 seconds, which can extend up to 300 seconds. Cloudflare WAF, however, supports up to 128KB payloads with a default timeout of 100 seconds, extendable to 6,000 seconds for Enterprise plans. These differences can significantly affect how each platform handles complex or resource-heavy requests.
| Metric | AWS WAF | Cloudflare WAF |
|---|---|---|
| Solve Rate (with PeakFO) | 99%+ | 99%+ |
| Response Time | Sub-second | Sub-second |
| Latency | Higher (due to redirects) | Low (edge-based) |
| Payload Limit | 64KB | 128KB |
| Default Timeout | 30 seconds (max 300s) | 100 seconds (max 6,000s) |
These differences in performance metrics and capabilities also play a role in how well each platform scales under heavy traffic.
Scalability Under High Traffic
Both AWS WAF and Cloudflare WAF are designed to handle high traffic, but their methods differ. AWS WAF is a cloud-native service with automatic scaling, earning a scalability sentiment score of 7.8 on PeerSpot. Cloudflare WAF, with its global edge network protecting over 27 million websites, scores a close 7.7. AWS WAF’s scalability benefits from being fully managed, while Cloudflare leverages its extensive edge infrastructure.
Cost efficiency under heavy traffic is another area where the platforms diverge. AWS WAF charges $0.60 per million requests, plus $0.30 per million requests for larger body sizes. These charges can escalate quickly with high traffic due to additional per-request and per-rule fees. Cloudflare, in contrast, offers flat-rate pricing starting at $25.00 per month, which includes free egress data. This makes it a more predictable and cost-effective option for applications experiencing high traffic.
For developers using PeakFO, both platforms offer unlimited scalability. API-based integrations eliminate the need to render full browser instances, enabling massive parallelization. Whether you're managing thousands or millions of requests daily, PeakFO ensures smooth operation without performance bottlenecks.
Pricing and Cost Efficiency
AWS WAF and Cloudflare WAF Pricing Models
Balancing cost with security is essential, especially in high-traffic environments where automated CAPTCHA solving becomes necessary.
AWS WAF follows a detailed pay-as-you-go pricing structure. It charges $5.00 per month per Web ACL, $1.00 per rule per month, and $0.60 per million requests processed. If CAPTCHA interactions are involved, there’s an additional fee of $0.40 per 1,000 attempts. For comprehensive bot protection, AWS Bot Control (Targeted) adds $10.00 per month and $10.00 per million requests, with the first million requests free.
On the other hand, Cloudflare WAF offers tiered subscription plans. The Pro plan starts at $20.00 per month, the Business plan costs $200.00 per month, and Enterprise plans are custom-priced. These plans include DDoS protection, bot detection, unlimited rules, and free egress data, which can lead to substantial savings.
For a high-traffic application handling 100TB of monthly traffic and 10 billion requests, AWS WAF costs are estimated at $17,055–$21,055 per month. This includes $6,000 for request processing, $3,000 for DDoS protection, and $8,000–$12,000 for CloudFront bandwidth. In comparison, Cloudflare’s Enterprise plan typically costs $2,000–$3,000 per month, offering a much lower price point for large-scale operations.
PeakFO's Pricing and Bulk Packages
PeakFO simplifies the process of solving CAPTCHA challenges with straightforward pricing plans.
It offers two main billing options: pay-per-solve pricing without balance expiry or discounted bulk packages tailored for high-volume users. These plans are designed to bring flexibility and savings to developers.
For Cloudflare WAF challenges, bulk packages range between $45.00 and $700.00, offering discounts of up to 42%. Each package includes a dedicated API key and a validity period of 30 days. For AWS WAF challenges on iOS and Android SDKs, packages are priced from $30.00 to $400.00, with discounts reaching as high as 50%. All packages are API-ready, enabling seamless scalability.
Pricing Comparison Table
| Cost Component | AWS WAF | Cloudflare WAF | PeakFO |
|---|---|---|---|
| Monthly Fee | $5.00/month per Web ACL | $20.00–$200.00/month (tiered) | Pay-per-solve or bulk packages |
| Request Processing | $0.60 per 1M requests | Included in subscription | N/A (solves challenges only) |
| CAPTCHA Costs | $0.40 per 1,000 attempts | Included | $30.00–$700.00 (bulk packages) |
| Bot Protection | $10.00/month + usage fees | Included in Pro+ plans | N/A |
| DDoS Protection | $3,000/month (Shield Advanced) | Included in all plans | N/A |
| Egress Data | Standard AWS rates | Free | N/A |
| Discounts | None | None | Up to 50% on bulk packages |
This breakdown underscores the cost dynamics that developers need to consider when managing large-scale traffic and CAPTCHA challenges. Each option offers distinct advantages depending on the specific needs and scale of the application.
Key Differences and Recommendations
Summary of Key Differences
AWS WAF and Cloudflare WAF take different approaches to protecting web applications. AWS WAF combines silent computational challenges with occasional visual CAPTCHA puzzles, while Cloudflare exclusively uses client-side signals and its Turnstile system, which verifies users without requiring interaction.
"Cloudflare does not use CAPTCHA puzzles or visual tests like selecting objects or typing distorted characters. All challenge types are lightweight, privacy-preserving, and optimized for real-world traffic." – Cloudflare Documentation
Pricing is another area where the two platforms diverge. Cloudflare offers flat-rate subscriptions starting around $20.00 to $25.00 per month, which include free egress data. AWS WAF, on the other hand, charges based on usage, which can lead to variable costs. AWS also provides native SDKs for iOS and Android, enabling programmatic handling of challenges, whereas Cloudflare focuses primarily on browser-based protection. Configuration efforts also differ: AWS WAF typically requires manual adjustments and technical expertise, while Cloudflare is designed to provide strong protection with minimal setup.
These differences highlight how each platform caters to different needs and use cases.
Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
The best choice between AWS WAF and Cloudflare WAF depends on your specific requirements. Factors like traffic patterns, integration needs, and your team's expertise should guide your decision.
Cloudflare's unmetered DDoS protection and free egress data make it a cost-effective option during high-traffic events. Its simplicity and efficiency are reflected in a 95% recommendation rate from industry experts. On the other hand, AWS WAF is well-suited for AWS-centric environments that require detailed "security-as-code" capabilities.
Mobile app developers may find AWS WAF particularly appealing due to its native SDK support, which allows programmatic challenge handling without interrupting API calls. Meanwhile, businesses with limited security expertise might prefer Cloudflare for its user-friendly interface and extremely low false-positive rate of 0.055%.
For organizations needing bulk CAPTCHA-solving capabilities, PeakFO offers discounts of up to 50% on AWS WAF challenges and 42% on Cloudflare WAF challenges. These solutions integrate easily via API, providing additional cost savings for large-scale operations.
Web Application Firewalls: How Cloudflare & AWS Protect Websites from 100 Million Daily Attacks!
FAQs
What is AWS WAF's proof-of-work mechanism, and how does it stop bots?
AWS WAF includes a proof-of-work mechanism aimed at detecting and blocking malicious bots. It works by presenting clients with a challenge, such as solving a CAPTCHA or completing a silent verification task. The system then assesses the response to determine whether the request is from a real user or an automated bot.
This approach helps AWS WAF reduce unwanted automated traffic, ensuring that only legitimate users gain access to your web application. It’s a practical way to maintain strong security, especially for environments with heavy traffic.
What makes Cloudflare WAF's Turnstile system stand out?
Cloudflare's Turnstile system offers a refreshing alternative to traditional CAPTCHA methods by being less disruptive and more intuitive. Instead of forcing users to solve puzzles or click on images, Turnstile works quietly in the background, ensuring a smoother user experience. It leverages advanced techniques like proof-of-work and API probing to differentiate between real users and bots without interrupting genuine visitors.
What makes Turnstile even more appealing is its versatility and simple integration. It can be implemented on any website, regardless of whether the site is part of Cloudflare's network. The system also adjusts the challenge difficulty in real time based on various signals, balancing strong security with minimal user friction. By prioritizing transparency in its privacy practices, Turnstile helps foster trust, making it a smart option for websites that value both security and ease of use.
Which WAF solution offers better value for high-traffic websites?
For websites with high traffic, Cloudflare WAF often proves to be a more budget-friendly choice than AWS WAF. One key reason is that Cloudflare offers features like built-in DDoS protection and advanced bot management without any additional charges, helping businesses cut down on security-related costs.
In contrast, AWS WAF applies separate charges for features like bot control and fraud prevention. Its pricing structure is also based on the number of rules, web access control lists, and the volume of requests, which can drive up costs as traffic grows. Moreover, Cloudflare's simple setup and automated security features eliminate the need for complex configurations, making it a practical and cost-efficient solution for handling large traffic volumes without compromising on security.